Introduction to robot vision
The purpose of robot vision is to locate the robot with respect to its external environment so that it can safely and efficiently perform its intended tasks. In mobile robotics, the external environment consists of the robot's destination, routes, obstacles, etc. Knowing its position and orientation with respect to these elements enables the robot to safely navigate towards its destination.
In industrial settings, the external environment mainly consists of obstacles and workpieces: parts to be assembled, panels to be drilled on, products to be inspected, etc. The objective of this Chapter is to present the algorithms and software tools to determine precisely the location of workpieces with respect to the robot, which will next enable the robot to perform its intended task – assembly, drilling, inspection, etc.
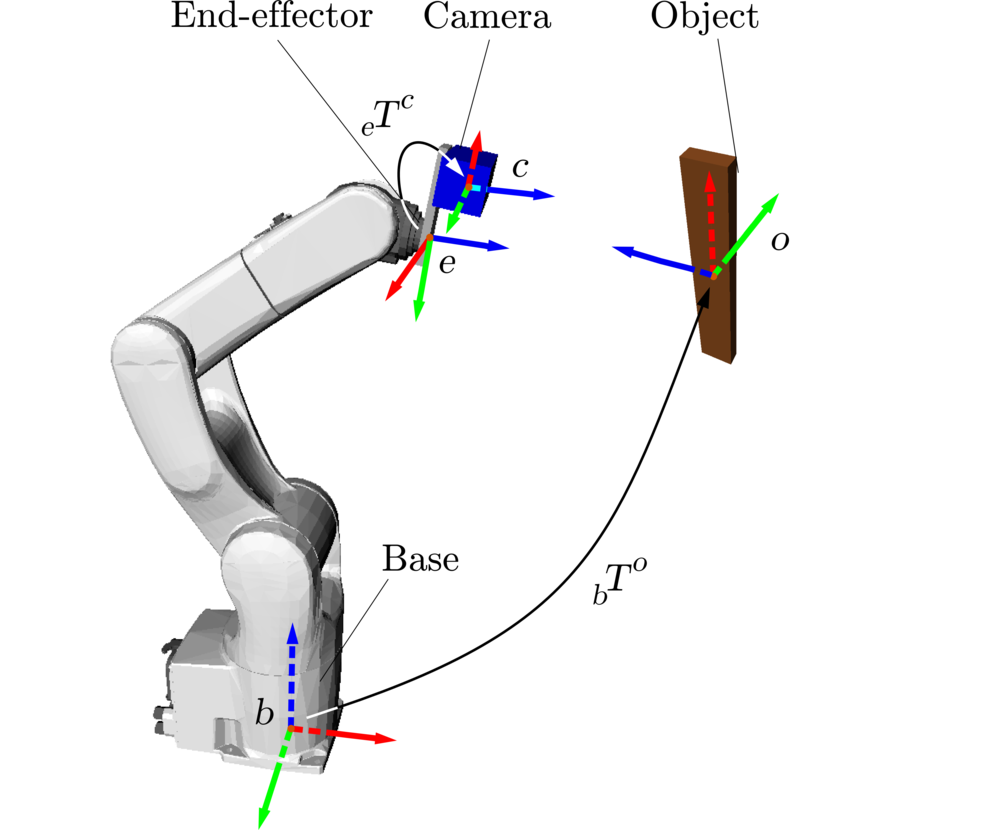
There are two main types of visual data: 2D (images) and 3D (point clouds). Section 2D vision presents basic algorithms, such as filtering or feature detection, and associated software tools to deal with 2D images. Section 3D vision introduces algorithms for object location using a 3D camera.