System: ROS, Gazebo
The Robot Operating System (ROS) is a flexible framework for writing and executing robot programs. It is a collection of tools, libraries, and conventions that aim to simplify the task of creating complex and robust robot behavior across a wide variety of robotic platforms.
ROS installation
Set-up your computer to accept software from packages.ros.org and set-up your keys following the steps described at http://wiki.ros.org/kinetic/Installation/Ubuntu
Now, install the ROS bare bones
command-line
# Installation
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get install python-wstool ros-kinetic-ros-base
# Initialize rosdep
sudo rosdep init
rosdep update
Create a ROS workspace
Let’s create a catkin workspace
command-line
source /opt/ros/kinetic/setup.bash
cd ~/catkin_ws/src
catkin_init_workspace
Even though the workspace is empty (there are no packages in the folder, just a single symbolic link) you can still build the workspace
command-line
cd ~/catkin_ws/
catkin_make
Before continuing, source your workspace file
command-line
source ~/catkin_ws/devel/setup.bash
To make sure your workspace is properly overlayed by the setup script, make
sure ROS_PACKAGE_PATH environment variable includes the path to your
workspace
command-line
echo $ROS_PACKAGE_PATH
This is the expected output
/home/USERNAME/catkin_ws/src:/opt/ros/kinetic/share:/opt/ros/kinetic/stacks
Configure your .bashrc
Every time you start a new terminal, the file ~/.bashrc will be sourced. When
you already have an opened terminal, you can source it manually running this
command
command-line
source ~/.bashrc
In order to use ROS, you need to source the ROS setup.bash file, therefore,
it's recommended to include the previous command in your .bashrc file.
You can do so by running this
command-line
echo "source ~/catkin_ws/devel/setup.bash" >> ~/.bashrc
Testing the installation
Let's try to run in a first terminal. Then, publish a message to the topic a second terminal. Finally, subscribe to the same topic and print it out the message in a third terminal:
command-line
# Terminal 1
roscore
# Terminal 2
rostopic pub -r 1 /some_topic_name std_msgs/String 'Hello World!'
# Terminal 3
rostopic echo /some_topic_name
ROS packages installation
For the sections where interaction with hardware components is required, we will simulate these components using Gazebo. More details can be found in the ROS architecture section.
ROS packages from source
Go to the source folder of your ROS workspace
command-line
cd ~/catkin_ws/src
Make sure that you have cloned the course repository.
Now, use the to install required packages from source repositories
command-line
wstool init .
wstool merge osr_course_pkgs/dependencies.rosinstall
wstool update
Install any missing dependencies using rosdep
command-line
rosdep update
rosdep install --from-paths . --ignore-src -r -y
If rosdep is unable to install python-termcolor, install it manually
command-line
sudo apt-get install python-termcolor
Now compile your ROS workspace:
command-line
cd ~/catkin_ws && catkin_make install
Dependencies
rosdep is very useful to install system dependencies but those dependencies
have to be included by the ROS community, therefore few packages need to be
install manually:
command-line
# Packages from Ubuntu repositories
sudo apt-get install blender openscad python-rtree
# Python modules
pip install control trimesh --user
Testing the installation
Let's try visualizing the robot using RVIZ
command-line
roslaunch osr_description visualize_robot_gripper.launch
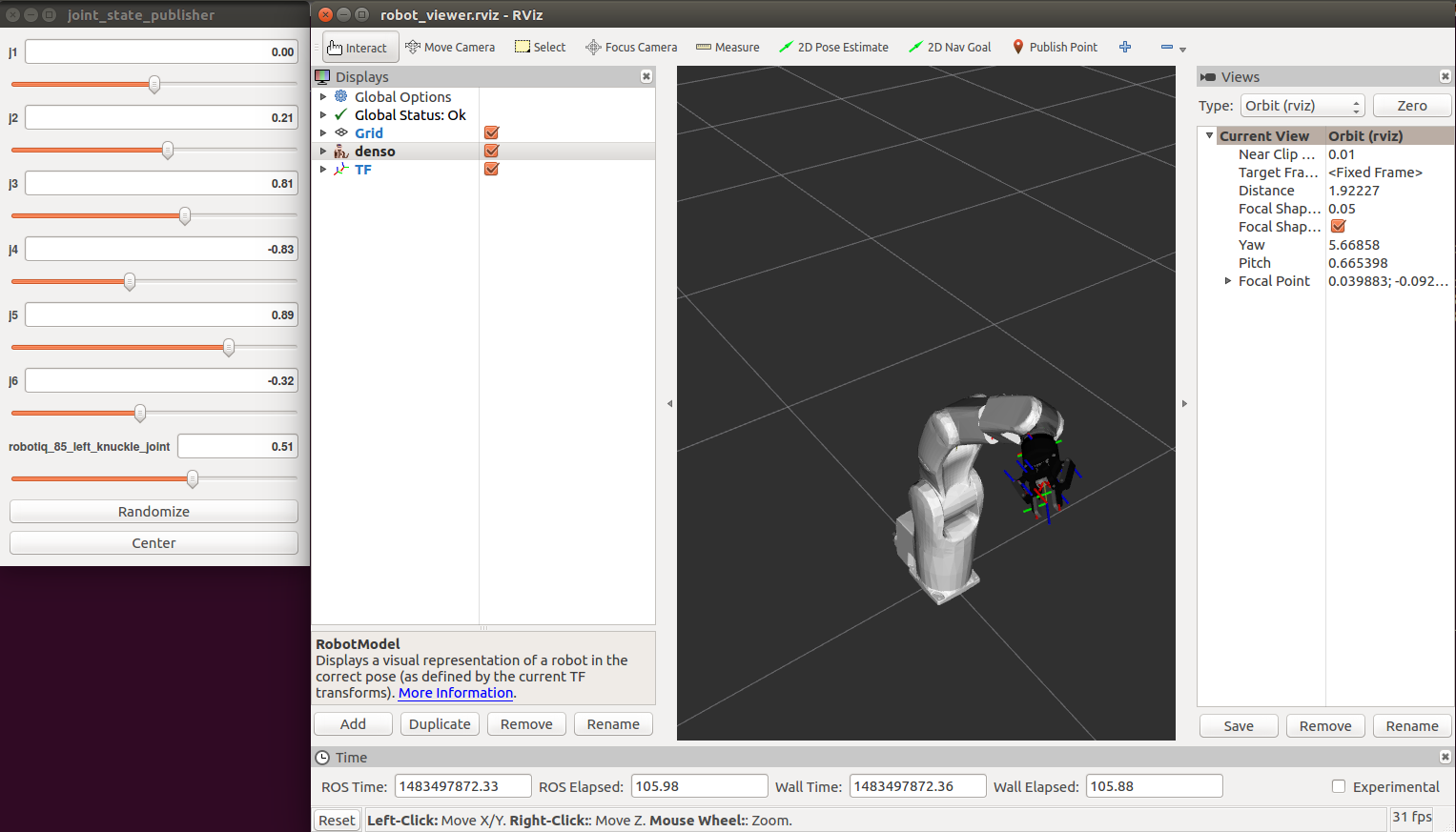
Play with the sliders to see how you can move the robot. This is a simple visualization where nothing is actually simulated. A simple test could be to move the robot to a configuration where it is in self-collision.
Finally, check that you can run the gazebo simulation:
command-line
roslaunch osr_gazebo robotic_setup.launch
Note: Gazebo takes for ever loading
The first time you run gazebo, it will download several models available online. You may want to start first gazebo alone and give it time to download the models:
command-line
gzserver --verbose
Note: Gazebo failure
In case of failure starting the simulation, check the system requirements for Gazebo. If your computer does not have a dedicated video card, it is likely that you will not be able to run the graphical interface. Try setting the parameter to false
command-line
roslaunch osr_gazebo robotic_setup.launch gui:=false
To learn more about this topic
Take a look at the ROS Tutorials.