System
Putting together the different hardware components of a robotic system requires a versatile and robust software architecture.
In this course, we propose an architecture that runs on top of the Robot Operating System (ROS). This allows us to conveniently integrate all the tools discussed in the previous chapters such as OpenRAVE, OpenCV and the Point Cloud Library (PCL).
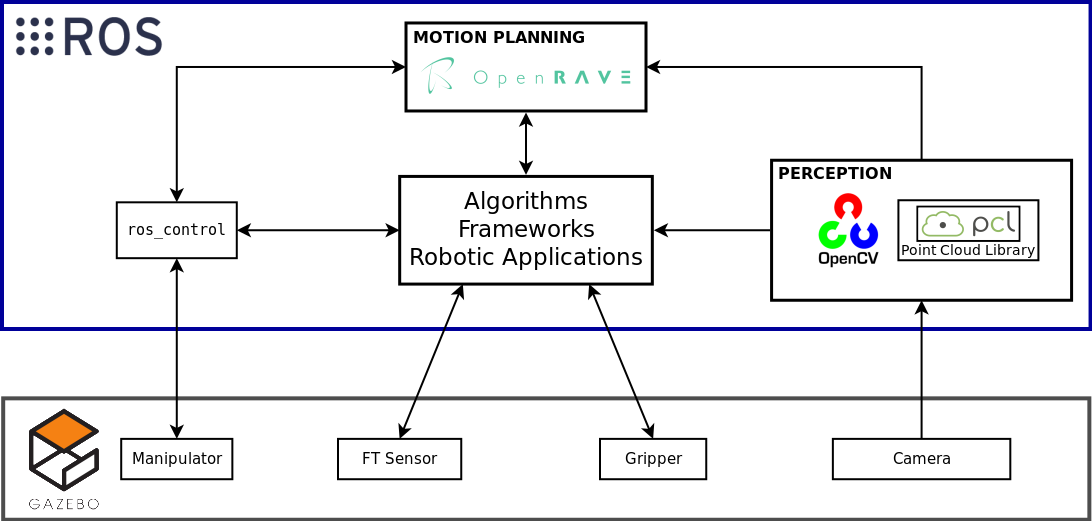
The figure above shows a representation of the software architecture. The simulation of the hardware components is done using Gazebo. It is a multi-robot simulator in a 3-dimensional world, with a robust physics engine, high-quality graphics, and convenient programmatic and graphical interfaces. It comes with advanced plugin-interfaces that can be used to simulate the sensors feedback and plausible interactions between objects.
For the propose of this course, we will be simulating the following components in Gazebo:
- Industrial manipulator: Denso VS-060
- Parallel-jaw gripper: Robotiq 85 Gripper
- Generic force/torque sensor
- Generic 3D camera